Aims and Scope
 Advances in Mobile Learning Educational Research (AMLER) (eISSN: 2737-5676) is an open access, international, refereed journal that aims to increase knowledge and understanding of how mobile technology can enhance education by the publication of high-quality research, which extends theory and practice. We welcome research papers on mobile technology's pedagogical uses, where the focus is broad enough to be of interest to a broader education community.
Advances in Mobile Learning Educational Research (AMLER) (eISSN: 2737-5676) is an open access, international, refereed journal that aims to increase knowledge and understanding of how mobile technology can enhance education by the publication of high-quality research, which extends theory and practice. We welcome research papers on mobile technology's pedagogical uses, where the focus is broad enough to be of interest to a broader education community.
We also welcome:
(1) systematic review papers and meta-analyses that include straightforward research questions, a framework of analysis, and conclusions that reflect the paper's aims;
(2) studies that focus on teaching and learning in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) and educational robotics;
(3) studies that address specific challenges in improving students’ achievement, approaches used to motivate and engage students, and lessons learned from changes in curriculum and instruction based on educational technology in general.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to the following:
• M-learning Educational Technology
• M-learning Educational Philosophy and Theory
• M-learning Education Innovation Management
• M-learning Educational Psychology
• M-learning Educational Policy
• M-learning Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis
• M-learning Educational Economics
Announcements
Indexed by Academic Databases
2021-04-12
Advances in Mobile Learning Educational Research is indexed in Scilit, BASE, J-Gate, EuroPub, Dimensions, Crossref, Google Scholar, Baidu Scholar, NLB of Singapore, etc.
Current Issue
Research Article
Currently, one of the challenges of higher education is to achieve the success of its students personally and professionally, emphasising improvement in technological, ethical, and academic areas that characterise human beings for success. Therefore, higher education must change the traditional way of training to a more humanistic approach framed in the digital era to solve social problems assertively. This research aims to generate comprehensive training guidelines from ethical research associated with Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and Artificial Intelligence to contribute to developing reflective critical thinking, maturity, and responsibility of individuals who will solve social problems. This study is based on Siemens' theory of connectivism (2004), Kohlberg's theory of moral development (1970), and Bandura's social learning theory (1974). Under the interpretive phenomenological approach, the applied methodological route is qualitative, focused on realities addressed from the context of transformation, using the documentary review technique. The inquiry led to the conclusion of the importance of conducting ethical research processes within technology in higher education to provide the student comprehensively with the knowledge and skills for successful integration into society.
The effect of mobile application to promote learning English for primary school students
This study aims to investigate the impact of mobile learning apps on primary school students' motivation and performance in English using Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. Monotonous traditional education lowers student motivation, lowering student performance in English. This will also impact their performance in English. Mobile learning applications built on Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning may be one way to increase students' motivation, which will help them solve problems more effectively and boost their performance. A pre-experimental study design was used, in which one group was examined with a comparison within a single group observed through time in the control group. A primary school's 26-year-five students were the samples discovered through purposive sampling. A questionnaire examined the effectiveness of motivation. In the meantime, students' performance was evaluated using an achievement test. Validity and reliability tests have been conducted on each instrument. To examine the impact of motivation and performance, a Wilcoxon Signed Rank-test is used to compare the mean before and after the intervention. During the intervention, a semi-structured interview was undertaken to learn more about how students perceived Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning-based mobile learning apps. The data from the interviews were analysed using thematic and coding analysis. As a result, the intervention can improve student performance in primary school English with significant mean changes, supported by the data from encouraging responses from the interview session.
Teachers' perspectives on artificial intelligence in education
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various aspects of society, including education. Understanding teachers' perspectives on this disruptive technology is essential, given its potential to revolutionize the teaching and learning process. A comprehensive study involving 74 educators utilized the Opinion Scale on Artificial Intelligence in Education to gather valuable insights. The research outcomes reveal a predominantly favourable view of AI in education, albeit accompanied by significant apprehensions regarding ethical and privacy-related issues. This study contributes significantly to the ongoing discourse on the role of AI in education, emphasizing the necessity for a balanced approach that maximizes the benefits of AI while ensuring the protection of the rights and interests of all stakeholders.
This study assessed the effectiveness of AI and AI-related technologies in the daily educational activities of undergraduate students in a modern and diversified university environment. The participants were 13 undergraduate Indonesian students participating in a mobility program for two weeks in Malaysia. A survey questionnaire designed with the help of the existing literature and ChatGPT, which includes ten (10) structured items and seven (7) open-ended questions, was used to collect the data. The relevant SPSS tests were used to analyze the data. Based on the results, of all 13 participants, 12 (92.3%) of them already experienced AI in their daily educational activities, and there were strong positive correlations between the attitudes toward AI and AI experiences, and attitudes toward AI and the effects of AI on education attributes, with correlation scores of .663 and .833 respectively. Based on the participant's answers to the qualitative questions, most of them believed that AI and AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, are helpful in daily educational activities and help them gain information regardless of time and space limitations and do their university-related assignments quickly. Based on the results, AI and AI-related technologies could transform different aspects of modern education.
Tutorials and mobile learning in higher education: Enhancing and accessibility
This comprehensive paper delves into two vital facets of contemporary higher education. The first segment investigates the transformative force of mobile learning (m-learning), elucidating its far-reaching impact on the educational landscape. Offering unprecedented flexibility and accessibility, m-learning redefines the dynamics between students and educators. The exploration navigates through potential benefits, challenges, and broader implications, providing a nuanced understanding of the evolving landscape of higher education in the digital age. The second segment focuses on the impact of active teaching in a first-year class at the National Engineering School of Carthage (ENICarthage) in Tunisia. Active teaching, recognized for engaging students in the learning process, is scrutinized for its effectiveness in enhancing theoretical understanding and graded assignment performance. This research introduces a dynamic dimension by incorporating mobile learning and tutorials as integral components of active teaching strategies. With its technological leverage, mobile learning aims to enhance student engagement, while advanced tutorials feature simulation functionality for an immersive learning experience. Through statistical analysis, the paper contributes to a nuanced comprehension of the positive influence of active teaching on academic achievements, offering practical insights into the application of active teaching methods and their potential benefits for enhancing student learning outcomes. This synthesis thus presents a holistic view of the dynamic interplay between mobile learning and active teaching in shaping the contemporary higher education landscape.
Nowadays, mobile phone usage is increasing, especially among children and adolescents. Mobile phones can offer a multitude of advantages, such as instant communication, entertainment, and information. Of course, the frequency regarding mobile phone usage and exposure poses risks, such as mobile phone addiction. Adolescents now have their own mobile phone and use it most of the time without limitations, with the risk of becoming addicted. The purpose of this research is to examine the increased mobile phone use among high school students, which may lead to addiction, as a social problem related to the lack of social interactions. The research method of the survey is quantitative. The sample of the quantitative method consists of 110 adolescents attending high school, each one equipped with a personal mobile phone. Several conclusions were drawn about mobile phone addiction and its association with social factor and the networks of adolescents. Data showed that parental educational level and average family income positively influenced the likelihood of adolescent mobile phone addiction. In contrast, no association was observed in terms of gender with adolescents' mobile phone addiction. It was observed that parental networks and peer networks had a negative effect on adolescents' mobile phone addiction. The research findings point middle family income and parents with a higher education degree are factors associated with adolescent mobile phone addiction. Additionally organizational networks, peer networks and parental networks are associated with adolescents' mobile phone addiction. Our research presents some limitations but paves the way for future research for the findings to become enhanced.
Perspective
The reality of e-Learning: Success and failure of learning management system
A learning management system (LMS) is a digital learning platform for developing, delivering, and managing courses, learning resources, activities, and assessments (to name but a few). Traditional classroom-based, online, blended, and distance learning are all possible learning methods that could be executed in LMSs. Learning management systems and associated tools have brought significant benefits to higher education institutions worldwide, including improved content deliverability, accessibility, and retrievability. This is also valid in the case of Kathmandu University School of Education (KUSOED), Nepal. In 2011, KUSOED launched LMS and continued online and blended learning practices. The LMS follows a social constructivist approach to education, allowing educational stakeholders (parents, students, leaders, facilitators) to engage in learning activities to scaffold the learning experiences. However, the perception of LMS as only a management system for storing data limits the implications of fostering learning through a technology-integrated education model. This article aims to discuss the success and failure aspects of LMS in the context of the KUSOED. The discussion will cover various perspectives on LMS as an emerging learning technology and draw conclusions based on our experiences at KUSOED. For the success aspects of LMS, we discovered four factors: sign-in, resources and learning management, content management, and integration. Nevertheless, for the failure aspects, we found content creation and sharing, communicative features, course structures, learning engagement, and assessment. Overall, this research has implications for educational institutions, instructors, developers, and system providers. These stakeholders can make more informed decisions about implementing and using these systems to their fullest potential in learning.
Case Study
The research is conducted to solve the problem of students' motivation while m-learning, namely while Maritime English online courses on LMS MOODLE. Gamification techniques are listed in the paper. The advantages of m-learning with gamification are described. The following activities are listed to motivate and engage students in Maritime English m-learning: leaderboards, badges, points, levels, missions, maps, and scenarios. The research was conducted in higher maritime education institutions in Ukraine. The research results show the positive impact of gamification while m-learning on the formation of communicative competence of future ship engineers. The prospects of further research can be seen in analysing other m-learning techniques to raise the quality of Maritime English online courses (e.g. game-based learning, problem-based learning).
Review
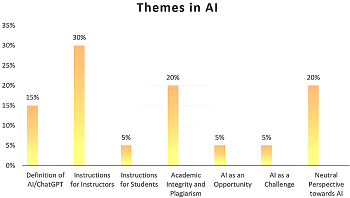
Since ChatGPT was released by OpenAI, an American company, in 2022 for the public, ChatGPT has become the talk of every town, as evident by its over 180 million users worldwide. This chatbot's ability to engage in human-like conversations, answer questions, and generate diverse content has sparked widespread debates across various fields, including education. In response to the growing rise and influence of ChatGPT, educators have contrasting opinions; some view ChatGPT as an opportunity, whereas others regard it as a challenge that needs to be addressed on time. In order to deal with the complexities caused by ChatGPT in the field of education, universities have formulated their policies on AI. Guided by the research question, "How does universities' policy on AI reflect academia's view toward ChatGPT?" this study attempts to review the AI policy of the nine academic institutions under the UT system of the United States. The primary goal is to understand the extent to which universities have adapted their policies in response to the challenges and opportunities posed by ChatGPT and how these policies reflect the broader sentiments within academia. To achieve this, this study reviews the universities' policies regarding AI using a qualitative data analysis methodology. The primary data sources include official policies, statements, and guidelines developed by the universities in response to the challenges and opportunities presented by ChatGPT. While reviewing the policies, the study determines whether ChatGPT is banned and why. Or embraced, and if so, in what ways? By examining these policies, the study aims to uncover the various approaches universities have taken to integrate or regulate the use of ChatGPT within academic environments. The thesis of this study is twofold. First, it seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of how US universities have responded to ChatGPT in the educational landscape. This involves identifying common themes, concerns, and strategies institutions employ to deal with the complexities introduced by this generative language model. Second, the study aims to contribute to existing scholarship by offering insights into how academia adapts to the influence of AI technologies like ChatGPT. This study examines the intersection of AI and education and the evolving nature of educational norms in the digital age by uncovering the diverse perspectives and approaches within university policies.
|
eISSN: 2737-5676 |





 Yulibeth Katiuska Guissepe Hernández, William Jesús Hernández Chávez, Sandra Moucharrafieh Moucharrafieh
Yulibeth Katiuska Guissepe Hernández, William Jesús Hernández Chávez, Sandra Moucharrafieh Moucharrafieh