2020-04-06
Aims and Scope
 Advances in Health and Behavior (AHB) (eISSN: 2630-466X) published biannually, is an international peer reviewed journal that publishes empirical and theoretical articles that apply sociological concepts and methods to the understanding of health and illness and the organization of medicine and health care.
Advances in Health and Behavior (AHB) (eISSN: 2630-466X) published biannually, is an international peer reviewed journal that publishes empirical and theoretical articles that apply sociological concepts and methods to the understanding of health and illness and the organization of medicine and health care.
Topics of interest include, but are not limited to the following:
• Health policy management and behavioral health
• Medical behavior, medical humanities and doctor-patient relationship
• Psychological behavior and quality of life
• Physical illness and mental health
• Public health and behavioral health
• The clinical diagnosis and treatment and behavior management
• Psychological behavioral health diagnosis and assessment
• Psychological behavior intervention and treatment
• Behavioral medicine and nursing and functional rehabilitation
• The behavioral medicine research
• Behavioral medicine and other interdisciplinary
• Smoke and health
• Drink and health
• Sleep and health
Announcements
Current Issue
Research Article
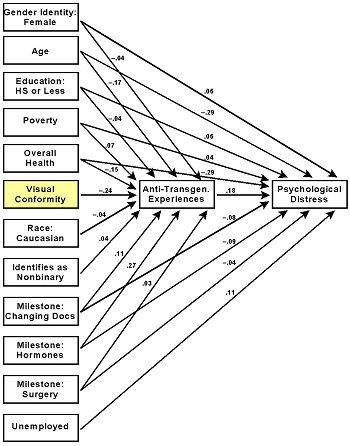
Purpose: Very little research has examined the issue of visual conformity with one's affirmed gender (commonly referred to as "passing'') among transgender persons. This paper examines this phenomenon and its relationship to psychological distress in a sample of transgender adults.
Methods: Data from the 2015 U.S. National Transgender Survey were used to examine the relationship between visual conformity with one's gender-of-identity (dichotomous measure) and overall level of psychological distress (scale measure) in a sample of 26,649 transgender Americans aged 18 or older. Multivariate and structural equation analyses were preformed to examine the data.
Results: 55% of the study participants reported attaining visual conformity with their affirmed gender. Visual conformity was related to psychological distress in bivariate analysis, but its effects were rendered statistically nonsignificant in a multivariate analysis. Structural equation analysis showed that visual conformity has a significant, inverse impact upon the number of anti-transgender experiences people incur and those experiences, in turn, are related directly and strongly to psychological distress.
Conclusions: Visual conformity with one's gender-of-identity is an important consideration when trying to understand the extent to which transgender persons experience psychological distress. Its effects operate indirectly, though, principally through their impact upon the number of anti-transgender acts of discrimination, harassment, and violence that people incurred.
| ISSN: 2630-466X Abbreviation: Adv Health Behav Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Alba Malara(Italy) Publishing Frequency: Continuous publication Article Processing Charges (APC): Click here for more details Publishing Model: Open Access |



 Hugh Klein, Thomas Alex Washington
Hugh Klein, Thomas Alex Washington

