Vol 1 No 1 (2026)
Research Article
Newton's law of universal gravitation and Einstein's General Theory of Relativity (GTR) face limitations in explaining gravitational anomalies and unifying fundamental physical forces. This study proposes that the gravitational constant G is not constant but distance-dependent (Gvar), establishing a unified theoretical framework for gravitational and nuclear interactions. We first derive the functional form of Gvar calibrated by planetary perihelion shifts, then analyze its impact on the physical unit system, and finally construct a matter--energy model based on the Primordial Energy Matrix (PEM) composed of force points. The results show that Gvar effectively explains gravitational anomalies (e.g., Pioneer anomaly, flyby anomalies) and achieves the unification of gravity with strong/weak nuclear and electromagnetic forces without introducing extra dimensions. The matter--energy model reveals that elementary particles (neutrons, protons, electrons) originate from vortices formed by PEM force points, and atomic/molecular structures are derived from the cascading combination of these vortices. This work provides a new perspective for understanding the nature of gravity and the origin of matter.
Case Study
A Space Health Education Curriculum for MD Students at the University of Melbourne (Australia)
Background: Since 2022, the University of Melbourne’s 4-year MD program has integrated a "Discovery" subject stream with core subjects and clinical placements. "Human Health in the Space Environment (HHiSE)"—one of seven MD1 flagship topics—launched in March 2022; the author curated its content and co-developed an engaging interactive online curriculum with learning designers via the flipped classroom approach.
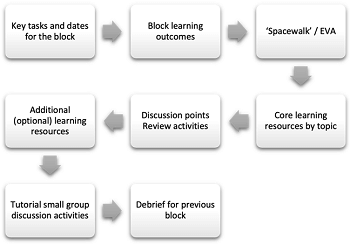
Description: This 24-week "mission-based" course is divided into systems-based blocks (e.g., Foundation, Cardiovascular, Respiratory). Students learn through "spacewalks" (learning resource sets), interactive tutorials, "Meet an Expert" virtual lectures, and the NASA/LEGO "Build to Launch" program (for teamwork training). It also explores "Space4Health" and translational space health research via "spinoffs," with three assessments focused on building students’ public science communication skills.
Discussion: This innovative course introduces students to human physiology in extreme environments and aerospace medicine, serving as a stepping-stone for training a space-enabled medical workforce. Its foundational template could be expanded to more space health subjects, adapted for public online access, or used for international collaborations to develop similar courses.
Review
From Fruit Flies to Genomics: Seventy-Five Years of Unraveling Spaceflight’s Impact on Life
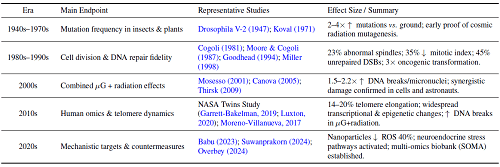
Over the past 75 years, studies on the biological effects of spaceflight has advanced from pioneering organism survival experiments to analyses integrating multi-omics technologies. This review adopts a historical perspective to synthesize these findings, with two core objectives: identifying recurrent mechanistic themes of space-induced biological alterations and evaluating strategies for preserving genomic stability during future deep-space exploration. The synergistic effects of weightlessness and ionizing radiation are primary drivers of heritable mutations, DNA damage clustering, and impaired repair fidelity. Longitudinal monitoring of astronauts, including twin-based comparative studies, has uncovered persistent molecular signatures such as altered methylation patterns, telomere dynamics changes, and immune regulation shifts. Targeted countermeasures developed include antioxidant supplementation, radioprotective pharmacology, genome editing, and synthetic biology-based therapeutics. Advances in portable sequencing and in-flight biomarker assessment enable real-time risk evaluation and adaptive health management during missions. As exploration extends to prolonged deep-space travel, ethical considerations like genetic data privacy and potential selection criteria gain prominence. This review integrates seven decades of cumulative discoveries, clarifying key targets and pathways for genomic stability protection. It provides a scientific foundation for personalized genomic monitoring, mechanistic risk assessment, and integrated prevention strategies, offering a roadmap for safeguarding biological integrity in future interplanetary expeditions.


 Hans Peter Weber
Hans Peter Weber