Vol 7 No 1 (2026)
Research Article
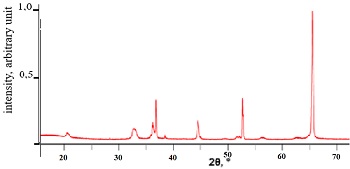
Lithium, sodium, and titanium hydrides have been synthesized. It has been found that lithium hydride is formed at a temperature of 650-700°C and a pressure of 12 atm. Lithium hydride contains 11 mass.% of hydrogen. Hydrogen desorption from lithium hydride occurs at a temperature of 700°C. Lithium hydride decomposes in water to form lithium hydroxide and hydrogen. Sodium hydride is formed at a temperature of 300-450°C with a hydrogen absorption level of up to 4 mass%. Hydrogen desorption from sodium hydride occurs at a temperature of 350-400°C. Titanium hydride is formed at a temperature of 600-650°C with a hydrogen absorption level of up to 4 mass%. Hydrogen desorption from sodium hydride occurs at a temperature of 450-650°C. Lithium, sodium, and titanium hydrides can be used in hydrogen storage and transportation processes.
Copper Sulfide Nanostructures as High-Capacity Anodes for Zinc-Ion Energy Storage Batteries
Zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) have emerged as promising candidates for large-scale energy storage systems due to their inherent safety, environmental friendliness, and cost-effectiveness. Among various anode materials, copper sulfide (CuS) has attracted significant interest owing to its high theoretical specific capacity, natural abundance, and low cost. However, practical application of CuS anodes remains limited by poor cycling stability and low electrical conductivity, which result in capacity fading over prolonged operation. This review summarizes the general methodology for developing CuS-based anodes for ZIBs, encompassing nanoparticle synthesis, material characterization, electrode fabrication, and electrochemical performance evaluation. Reported studies indicate that CuS can deliver specific capacities ranging from 350 to 700 mAh g⁻¹, with performance strongly influenced by synthesis route and electrode design. To overcome intrinsic limitations, recent research has explored nanostructuring, elemental doping, and hybrid electrode architectures, which have shown encouraging improvements in conductivity, rate capability, and cycle life. The review concludes with a discussion on current challenges and future perspectives, emphasizing the need for further optimization of CuS morphology, conductivity enhancement strategies, and interface engineering to enable its practical deployment in high-performance ZIB systems.


 M. S. Paizullakhanov, O. R. Parpiev, E. Z. Nodirmatov
M. S. Paizullakhanov, O. R. Parpiev, E. Z. Nodirmatov

