Vol 7 No 1 (2025)
Review
Using advanced scientific and risk-based approaches for analytical methods offers significant benefits. Quality by Design (QbD) is a systematic framework that emphasizes understanding and controlling both product and process elements. Adhering to the principles outlined in the ICH guidelines can considerably improve the quality of drug substances, vaccines, immune markers, and medicinal products. This compliance not only enhances product quality but also drives continuous improvement and innovation throughout the entire product lifecycle. Developing and regulating analytical methods are vital for maintaining high standards of product quality. By employing sophisticated scientific techniques and risk-based strategies, stakeholders can use various analytical methods to ensure the consistent production of high-quality active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Techniques such as size exclusion chromatography (SEC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gel electrophoresis, Western blotting, SDS-PAGE, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are essential for boosting industrial efficiency and reliability in the pharmaceutical sector. Each technique supports the rigorous testing and validation required for API production, ultimately facilitating the development of safe and effective medical products. Understanding the impact of variability on the performance and results of analytical methods is crucial. The QbD framework adopts a systematic approach that underscores the need to thoroughly understand and effectively manage various aspects of the product and its manufacturing processes—laying the groundwork for ongoing improvements and innovation throughout the product lifecycle. Additionally, strict development and regulation of analytical methods are key to achieving the highest standards of product quality. Fully grasping how variability influences the performance and outcomes of analytical methods is essential, as this understanding optimizes results and maintains consistent quality. Recognizing these dynamics enhances result reliability and supports the goal of delivering safer, more effective healthcare solutions.
Commentary
An Electronic Analytical Balance: A Key Instrument in the Laboratory
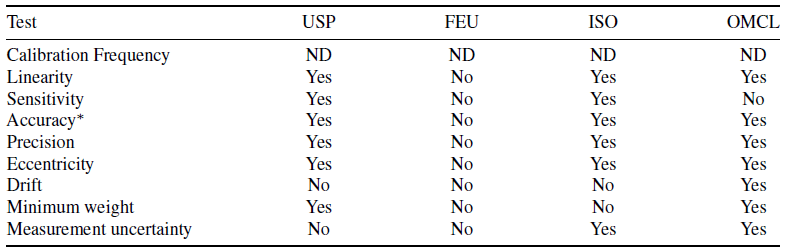
Digital analytical balances are crucial in laboratory settings for accurately determining an object's mass. The precision of these balances highlights their importance in scientific endeavours. This study explores the significance of achieving equilibrium and other relevant concepts in analytics to advance the field. It examines a range of factors, with the balance as a focal point: identifying analytical challenges, where the balance plays a critical role in pinpointing potential areas of error or inconsistency; aligning well-established constitutive and operational concepts with these challenges; evaluating new theories; and developing clinical and laboratory tests based on current knowledge. This overview is a condensed compilation of data—sourced from pharmacopoeias and gathered via search engines such as Google Scholar, PubMed, and Scopus. The concept of balance is introduced not only as a physical principle but also as a pervasive notion that extends across various aspects of our work. The diverse array of motor skills is explored, accompanied by an essential scale for assessing them, shedding light on the depth and intricacy of the topic.



 Ritu Tiwari, Gaurav Sanjay Mahalpure, Shaily Tyagi, Meenakshi Dahiya, Vivekanandan Kalaiselvan
Ritu Tiwari, Gaurav Sanjay Mahalpure, Shaily Tyagi, Meenakshi Dahiya, Vivekanandan Kalaiselvan